Financing and investors
We create long-term value based on sustainable strategy
In order to keep investing and consolidating its position of leadership in the energy and environment sectors, the company continues to strengthen its financing model, a model which ensures the company’s solvency and viability. Due to the international financial crisis, access to financing has posed a significant challenge for companies in recent years; however, thanks to its business model and potential for growth, Abengoa has been able to access sources of financing that allow the company to successfully move forward in conducting its activities.
Abengoa’s business model is grounded in the development of new businesses, maintaining a highly competitive team of people, geographical diversification and R&D investment effort. In short, Abengoa embraces an unwavering commitment to a sustainable business strategy focused on creating long-term value, which makes the company’s business model attractive to potential investors.
In terms of financing, Abengoa has two key objectives: accessing a level of financing that will enable the company to continue to enjoy sustainable growth while gradually reducing debt.
Accomplishing these two objectives requires a high degree of financial flexibility and a stable shareholding. Financial flexibility is needed to be able to access fixed income and equities markets in order to balance the business structure with the source of financing, build an investor base enabling access to more stable capital markets and diversify the financing structure towards more competitive global sources. Continuing to count on stable shareholding is vital to Abengoa because its business model, which is heavily based on technology and R&D and innovation, requires investors that are committed to the company’s strategy and long-term vision.



Abengoa’s financing model
Abengoa has a financing model that is backed by the company’s solid business model and long-term vision. As a product of both this and the solvency of its operations, the company has continued to finance itself in the principal markets in which it operates through the following mechanisms:
- Capital markets (37 % of financing). Currently accounting, 72 % of Abengoa’s corporate financing, these mostly include seven high-yield bonds, two convertible bonds and a short-term commercial paper program. This is corporate-secured debt.
- Loans held with financial institutions, non-recourse debt in process (15 % of financing). The main source of corporate financing is a syndicated loan via a banking pool with a five-year maturity. Financing is also secured through other lending institutions, including Instituto de Crédito Oficial (ICO), a state-owned bank, and a variety of export credit agencies. This type of debt has the same guarantees as corporate debt.
- Long-term non-recourse financing associated with concession-type projects (48 % of financing). This type of financing is generally used as a means of building or purchasing an asset, taking as collateral exclusively assets and cash flows of the company or group of companies conducting the activity linked to the asset in question. This constitutes long-term financing of concession projects, which are secured by the projects themselves. Included in this type of debt is non-recourse financing in process which serves as bridge financing until the long-term non-recourse debt has been closed. From the standpoint of guarantees, both bridge financing and long-term financing (project finance) enjoy the same technical guarantees in relation to price, time and performance. The difference is that bridge financing also has a corporate guarantee from the project sponsor to cover the eventuality of a delay in project-finance closing.
Note 1 Convertible bond: a fixed-income financial asset that can be converted into a specific number of shares of the issuing company’s stock through a capital increas.
Note 2 Banking pool: document which provides detailed information on the financial operation risks of a physical or legal person with respect to banking instit.
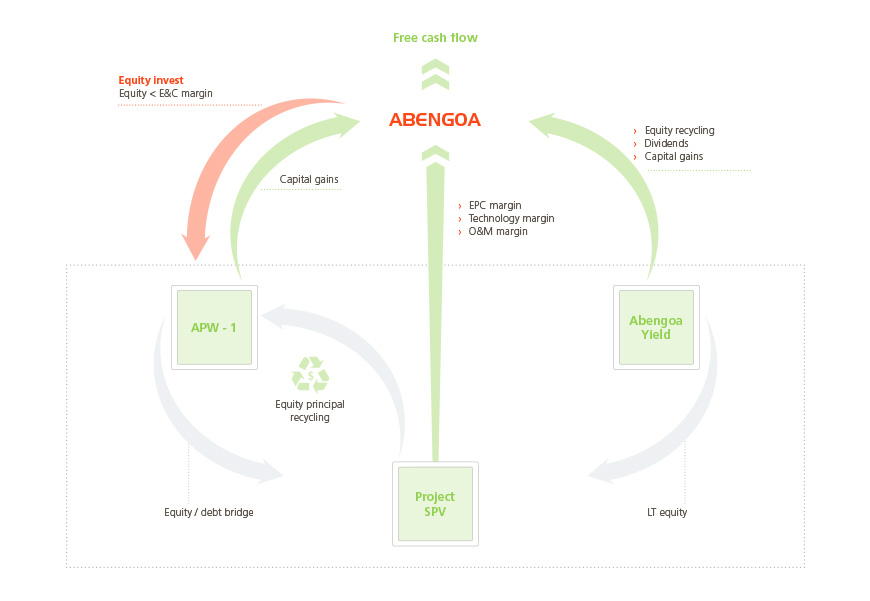
Abengoa Yield
Abengoa Yield is a company listed on the NASDAQ exchange that has its own sources of financing which are separate from those of Abengoa. Abengoa Yield invests, manages and acquires renewable energy, conventional power generation and power transmission line assets, as well as other assets under concession. The company currently owns and manages 13 concession assets and holds a pre-emptive purchase right on certain Abengoa assets. Abengoa Yield has long-term non-recourse financing in all of its concession assets and access to capital markets and bank financing.
Abengoa Projects Warehouse 1
Abengoa Projects Warehouse 1 is a newly created company which, together with the energy infrastructure investor EIG Global Energy Partners (EIG), will acquire a portfolio of Abengoa projects in the construction phase, including renewable and conventional power generating, power transmission and water management assets in different geographic regions, including the U.S., Mexico, Brazil and Chile. The aim is to build up sufficient funds to have permanent capital to help finance the construction of new concession projects awarded to Abengoa. Thanks to Abengoa Projects Warehouse 1, Abengoa’s business and financing model will be more efficient as projects will become less costly to finance and construction can get under way sooner, meaning earlier asset start-up and dividend generation.
2014 saw a significant rise in socially responsible investor interest in Abengoa
Socially responsible investor market
Abengoa’s affinity with socially responsible investors, also referred to as ESG (Environment, Social and Governance) investors, constitutes assurance for the company’s long-term growth.
The company’s responsible business management has been acknowledged by a variety of rating agencies and sustainability indexes.

(1) In its first participation in the Corporate Sustainability Assessment to be included in the Sustainability Yearbook, Abengoa has obtained a score of 77 points.
In 2014, the company actively participated in three conferences of this kind, and in June staged a roadshow ahead of the issuance of its first green bond aimed at ESG investors in the high-yield company spectrum. Abengoa seeks to increase its base financing among these investors with the aim of continuing to grow in the long term, optimizing financial costs and diversifying sources of financing.
Green bonds
In September 2014, Abengoa, through its Abengoa Greenfield, S.A. subsidiary, launched a green bond offering in euros and U.S. dollars for an amount equivalent to €500 M and maturing in 2019. This operation was intended for both investors traditionally interested in high-yield bonds3 and buyers of socially responsible investments with a specific mandate or portfolio allocated to purchasing green bonds.
The net proceeds obtained have been used to partially or wholly finance, until long-term financing funds are obtained, green projects which meet the eligibility criteria approved by Vigeo, a European agency dedicated to evaluating sustainable performance. Vigeo issued a favorable outside opinion with respect to the issuance of these bonds.
Eligibility criteria
In keeping with Abengoa’s CSR strategy and policy and its commitment to sustainability and the fight against climate change, projects financed through green bonds must belong to one of the following categories:
- Renewable energy
- Power transmission and distribution
- Energy efficiency
- Water management
- Water transport and distribution
- Bioenergy
- Waste to energy
And these projects must meet a set of environmental, social and governance criteria, compliance with which is to be verified using a series of indicators that are audited by an independent third party and published by Abengoa in the CSRR each year throughout the life of the bond.
Addressed in the “Green Bond” Appendix D is detailed all the information related to the projects that have been financed with the green bond: project description, fund allocation, environmental and social outcomes ,and responsible management indicators. All the information has been verified by PwC4.
Note 3 High-yield bonds: fixed-income financial assets that generate high yield by investing in bonds with a lower credit rating than investment-grade corporate bonds. They offer a higher yield in exchange for an also higher risk of default.
Note 4 The PwC verification report is published in the chapter titled “External Verification”.
Transparent communication
The company continued to further its commitment to providing investors and analysts with the information needed to carry out a complete analysis of the company’s performance in different areas (economic and financial, social and environmental). Key for Abengoa is continual enrichment of the information the company provides to its stakeholders, offering increasingly more comprehensive content in line with their requirements, thereby building stronger relationships while enhancing dialog channels in order to provide an optimal flow of information.

Manuel Sánchez Ortega, executive vice chairman. Analyst day. ![]()
Over the course of 2014, the company placed particular emphasis on communicating with its investors through the following initiatives:
- Conducting five roadshows5 in five countries: the U.S., the United Kingdom, France, Canada and Italy.
- Attendance at 42 conferences in 12 cities: Madrid, London, Paris, Copenhagen, Frankfurt, Cascais, Lyon, New York, Boston, New Orleans, Miami and San Francisco.
- Visits to financial centers in London, New York, Paris, San Francisco and Milan.
In May, Abengoa hosted its 8th Annual Analyst and Investor Day in New York and London. The event had a great turnout, particularly in New York, where more than 100 people were in attendance, illustrating Abengoa’s increased visibility in the U.S. market. The types of questions formulated by investors and analysts showed that they are now more aware of the company’s financial markets.
With a view to addressing stakeholder needs, the company has also set itself the objective of increasing the number of visits to and stepping up communication in places that have been identified for engaging potential investors.
Note 5: Roadshow information session provided to investors and analysts by the company in order to present financial results.
Shareholding structure
Abengoa is a listed company with share capital totaling € 91,798,9006, represented by 825,562,690 fully subscribed and paid-up shares belonging to two different classes:
- 84,243,640 shares belonging to Class A7, each with a par value of € 1 and individually conferring 100 votes.
- 755,526,080 shares belonging to Class B8, each with a par value of € 0.01 and individually conferring one vote.
Class A and Class B shares are admitted for official trading on the Madrid and Barcelona Stock Exchanges and on the Spanish Stock Exchange Interconnection System9 (Continuous Market). Class A shares have been admitted for trading since November 29, 1996, and Class B shares have been admitted for trading since October 25, 2012. Additionally, the ADS (American Depositary Shares) constituted upon B shares are admitted for official trading on the U.S. NASDAQ electronic securities exchange.
The company’s shareholding structure is as follows:
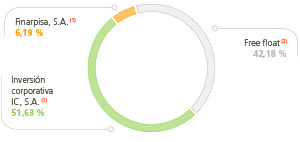
(1) Corporate Investment Group.
(2) Free Float:the portion of shares of a corporation that are traded freely on the market without being in the hands of a shareholder.
Note 6 November 4, 2014 is the date of the last Abengoa share capital modification
Note 7 Class A Shares: shares with a right to 100 votes per share (+ info)
Note 8 Class B Shares: shares with a right to 1 vote per share (+ info)
Note 9 Spanish Stock Market Interconnection System (SIBE): electronic platform for trading variable income securities on the national stock exchanges and which provides real-time information on security activity and trends
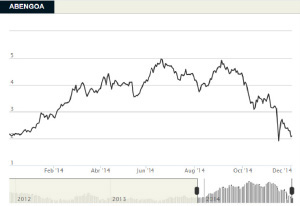
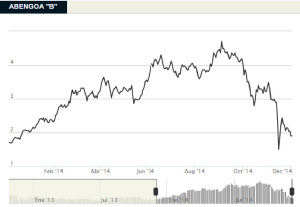
Share performance
Abengoa saw highly positive stock market evolution in 2014 through to September, recording an appreciation in value of over 100 % up until that time, given that the company’s stock began the year at € 2.00 per share and went on to reach € 4.69 per share.